Bio-Algae Concentrates (BAC), unlike many supplements on the market, is not a conglomeration of separate, isolated vitamins and minerals, or extracted and concentrated ingredients bound together and compressed with fillers in a pill. BAC is actually a whole food containing just four micro-algae carefully grown under special conditions with strict control of light sources, harvested, preserved and proportioned: Spirulina Pacifica, Spirulina Plantentis, Dunaliella and Heomatoccoccus Pluvialis for its high asthaxanthin content.
Together these algae contain thousands of naturally occurring nutrients like proteins, vitamins, minerals, chlorophylls, antioxidants, fatty acids, enzymes and lots more. So simple, yet read on to find out the extraordinary diversity of its nutrients!
The nutritional mission of BAC
With BAC no attempt is made to measure up or compare its nutrients to the Required Daily Allowances (RDA) suggested by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). BAC is not a vitamin, not a mineral, not an antioxidant, not an enzyme or not even a supplement; BAC is all of the above. That is made possible only because BAC is just a natural whole food, though an extraordinary whole food. The purpose of BAC is that of a food, that is to feed the body with required nutrients. We know today that the principal nutrients for prevention of cancers are found in eating a mix of colourful fruits and vegetables (American Cancer Society). Those nutrients are the mixed antioxidants, carotenoids, chlorophylls and other phytonutrients that are found in those fruits and vegetables.
Proteins
Some algae in Bio-Algae Concentrates (BAC) have the highest usable (90% NPU) protein content of any natural food (65%); far more than meat and fish (15-25%), soybeans (35%), dried milk (35%), peanuts (25%), eggs (12%), grains (8-14%) or whole milk (3%).
BAC’s algae have no cellulose in their cell walls, being composed of soft mucopolysaccharides. Their proteins are 85 to 95% digestible and assimilated. This high digestibility rate is especially important for people suffering from intestinal malabsorption. Typically, older people have greater difficulty digesting complex proteins, and many are on restricted diets.
Amino Acids
Bio-Algae Concentrates (BAC) contains all known essential and non-essential amino acids in high availability or non limiting form.
Amino acids are all about quality. Protein is composed of amino acids. Essential amino acids cannot be manufactured in the body and must be supplied in the diet. Non-essential amino acids are needed too, but the body can synthesise them. Essential amino acids, plus sufficient nitrogen in foods, are needed to synthesise the non-essential amino acids. A protein is considered complete if it has all the essential amino acids. Spirulina in BAC is just that, a complete protein.
The body requires amino acids in specific proportions. If a food is low in one or more amino acids, those amino acids are called limiting amino acids, and the body cannot use all the amino acids completely. The most complete and ideal proportion of amino acids can be found in BAC because of its mix of carefully selected algae. BAC complements vegetable protein and increases the amino acid quality if eaten within several hours of other foods. A good portion of the daily essential amino acid required for a typical adult can be supplied by eating BAC daily.
The following eight essential amino acids are found in BAC:
- ISOLEUCINE: Required for optimal growth, intelligence development and nitrogen equilibrium in the body used to synthesise other non-essential amino acids.
- LEUCINE: Stimulator of brain function, increases muscular energy levels.
- LYSINE: Building block of blood antibodies, strengthens circulatory system and maintains normal growth of cells.
- METHIONINE: Vital lipotropic (fat and lipid metabolizing) amino acid that maintains liver health. An anti-stress factor, it calms the nerves.
- PHENYLALANINE: Required by the thyroid gland for production of thyroxine which stimulates metabolic rate.
- THREONINE: Improves intestinal competence and digestive assimilation.
- TRYPTOPHANE: Increases utilisation of B vitamins, improves nerve health and stability of the emotions. Promotes sense of calm.
- VALINE: Stimulates mental capacity and muscle coordination.
Spirulina alone supplies ten of the twelve non-essential amino acids. “Non-essential” does not mean that these amino acids are not needed by the body, but merely indicates that the body can synthesise them itself if it needs to do so, provided the appropriate nutritional building blocks are available. Nevertheless, the body is better served if these excellent protein components are readily and totally available in dietary sources, since all the amino acids must be on hand as the cells manufacture enzymes, proteins, hormones, brain chemicals and the other products of metabolism. Of the thousands of biochemical substances acting and interacting in the human body, not one is derived from a vacuum; the body is ultimately dependent upon nutrient intake for all of its functions.
The following are the non-essential amino acids supplied by BAC:
- ALANINE: Strengthens cellular walls.
- ARGININE: Important to male sexual health as seminal fluid is 80 percent arginine. Also helps detoxify the blood.
- ASPARTIC ACID: Aids transformation of carbohydrates into cellular energy.
- CYSTINE: Aids pancreatic health, which stabilises blood sugar and carbohydrate metabolism. Has been used to alleviate some symptoms of food allergy and intolerance.
- GLUTAMIC ACID: With glucose, one of the principal fuels for the brain cells. Has been used to reduce the craving for alcohol and stabilise mental health.
- GLYCINE: Promotes energy and oxygen use in the cells.
- HISTIDINE: Strengthens nerve relays, especially in the auditory organs. Has been used to reverse some cases of deafness.
- PROLINE: A precursor of glutamic acid.
- SERINE: Helps form the protective fatty sheaths surrounding nerve fibers.
- TYROSINE: Slows ageing of cells and suppresses hunger centres in the hypothalamus. Can be synthesised from phenylalanine. Involved in proper colouration of hair and skin, including protection from sunburn.
Vitamins
Bio-Algae Concentrates (BAC) contains the array of vitamins that most living beings need to carry on metabolic processes.
Not only does BAC contains all vitamins, including a full Vitamin B Complex, vitamins A, D, K, E & C, BUT it also contains all co-dependent nutrients for these vitamins to be functional and active for human assimilation.
As BAC is a complete and balanced food, you don’t have to worry about dosages. You cannot make a mistake with mixing and matching like you can with isolated and separate vitamins and minerals. You don’t even have to worry about taking it with or without foods. All you need is water alongside. When you take BAC, you automatically get completeness and perfect ratios. BAC is known for balance and synergy between of the vitamins and minerals that your body needs. The way nature makes nutrients cannot be replicated by chemistry, and it is not likely to be replicated ever. A small amount of vitamin C occurring in a green pepper is tremendously more nutritionally functional than 1,000 mg of ascorbic acid from a bottle. Furthermore, when you take vitamin supplements, you are taking risks with mixing and matching isolate and synthetic compounds that fall in the chemical category.
You CANNOT sustain life by eating multi-vitamins and minerals as supplements.
You find in BAC the vitamin: A, B C, D, E, K, folic acid, inositol, and biotin:
- VITAMIN A: Necessary for growth & repair of body tissues; helps maintain smooth, soft disease-free skin; helps protect the mucous membranes of the mouth, nose , throat & lungs, thereby reducing susceptibility to infections; protects against air pollutants; counteracts night-blindness & weak eyesight; aids in bone and teeth formation. Current medical research shows that foods rich in Beta Carotene will help reduce the risk of lung cancer & certain oral cancers. Unlike Vitamin A from fish liver oil, Vitamin A from BAC is non-toxic.
- PYRIDOXINE or B6: Involved in breakdown and assimilation of protein. Protects cardiac health, reduces oedema and stabilises female hormone levels. Dr. Carl Pfeiffer has demonstrated that B6, together with the mineral zinc, can cure some forms of schizophrenia.
- BIOTIN: An enzyme that carries CO, during certain biochemical reactions involved in carbohydrate metabolism. Also acts as a co-enzyme in the assimilation of other B-complex vitamins. Biotin is destroyed by eating raw egg whites and some kinds of raw fish.
- COBALAMIN or B12: The most difficult of all vitamins to obtain from vegetable sources. Bio-Algae Concentrates (BAC) is extremely rich in this rare vitamin, containing 250 percent more than beef liver, previously thought to be nature’s richest source. A single serving of BAC easily exceeds the Recommended Daily Allowance of 1.5 to 3 mcg daily. B12 deficiency results in pernicious anaemia, nerve degeneration, premature senility, pronounced fatigue and mental illnesses resembling schizophrenia.
- PANTOTHENIC ACID: The “stress” vitamin, used by the adrenal glands, along with cholesterol and vitamin C, to manufacture cortisone and other steroids in response to physical and mental stress. Deficiency encourages sensitivity to allergy, infection and degenerative diseases such as arthritis and rheumatism. Ulcers and hypoglycemia have also been associated with shortage of this vitamin.
- FOLIC ACID: Essential to proper haemoglobin formation in red blood cells. Deficiency results in anaemia, poor growth, skin pigmentation disorders and premature greying of the hair.
- INOSITOL: Vital lipotropic nutrient that sustains liver health and helps detoxify carcinogens, particularly excess female hormones. Helps normalise blood cholesterol levels. With choline, inositol is used by the liver to manufacture lecithin. Inositol is the second most abundant vitamin in the body, after niacin. Recent studies indicate that inositol, with biotin, reduces loss of scalp hair.
- NIACIN: Also known as nicotinic acid and niacinamide, which is an alternative form, niacin is essential to mental health. Dr. Abram Hoffer, a renowned pioneer in orthomolecular psychiatry, has completely relieved schizophrenic symptoms using niacin. The Physicians’ Desk Reference, a pharmaceutical text used by doctors when prescribing medication, recognises niacin as an effective cholesterol lowering agent.
- RIBOFLAVIN or B2: The most common vitamin deficiency is that of riboflavin and results in cataracts, failing vision, watery eyes and uncontrollable eczema.
- THIAMINE or B1: A co-enzyme in the breakdown of dietary carbohydrates maintains levels of glucose in the blood. Deficiency results in weakness, cardiac damage, abdominal distention and poor oxygenation. Severe shortage results in death; critical toxemia develops from unmetabolised carbohydrate fragments.
- VITAMIN C: Essential for healthy teeth, gums & bones; helps heal wounds, scar tissue, & fractures; prevents scurvy; builds resistance to infection; aids in the prevention & treatment of the common cold; gives strength to blood vessels; aids in the absorption of iron. It is required for the synthesis of collagen, the intercellular “cement” which holds tissues together. It is also one of the major antioxidant nutrients. It prevents the conversion of nitrates (from tobacco smoke, smog, bacon, lunch meats, & some vegetables) into cancer-causing substances. According to Dr. Lines Pauling, the foremost authority on Vitamin C, Vitamin C will decrease the risk of getting certain cancers.
- VITAMIN D: Improves absorption and utilisation of Calcium and Phosphorous; required for bone and teeth formation; maintains a stable nervous system and normal heart action.
- TOCOPHEROL or vitamin E: Algae in BAC contains more vitamin E per gram than pure wheat germ. Its biological activity is 49% greater than synthetic vitamin E. Vitamin E protects heart and vascular health, promotes oxygenation of cells, and retards ageing.
Minerals and Trace Elements

There are more than 100 dietary minerals and trace elements detected in Bio-Algae Concentrates (BAC). When using specific element analysis, a certain amount of all of the known dietary minerals are detected in BAC.
Minerals are constituents of the bones, teeth, soft tissue, muscle, blood, and nerve cells. They are vital to overall mental and physical well-being. Minerals act as catalysts for many biological reactions within the body, including muscle response, the transmission of messages through the nervous system and the utilization of nutrients in food.
As important as vitamins are, they cannot be assimilated without the aid of minerals. Although the body can manufacture a few vitamins, it cannot manufacture a single mineral. All tissue and internal fluids contain varying quantities of minerals.
Since BAC is a food, its minerals occur in non toxic form as prepared by nature within the plant or in the case of BAC by the algae.
Here is a partial list of the principal minerals or trace minerals found in BAC:
Antimony, Arsenic, Barium, Beryllium, Bismuth, Boron, Cadmium, Caesium, Calcium, Cerium, Chromium, Cobalt, Copper, Dysprosium, Erbium, Europium, Gadolinium, Gallium, Germanium, Gold, Hafnium, Holmium, Iridium, Iron, Lanthanum, Lead, Lithium, Lutetium, Magnesium, Manganese, Mercury, Molybdenum, Neodymium, Nickel, Niobium, Osmium, Palladium, Phosphorus, Platinum, Pluminium, Potassium, Praseodymium, Rhenium, Rhodium, Rubidium, Ruthenium, Samarium, Scandium, Selenium, Silicon, Silver, Sodium, Strontium, Tantalum, Tellurium, Terbium, Thallium, Thorium, Thulium, Tin, Titanium, Tungsten, Uranium, Vanadium, Ytterbium, Yttrium, Zinc, Zirconium.
Next, you will find a value discussion of a few of the principal minerals found in BAC:
- CHLORIDE: Chloride ions have important physiological roles. For instance, in the central nervous system, the inhibitory action of glycine and some of the action of GABA relies on the entry of Cl− into specific neurons. Also, the chloride-bicarbonate exchanger biological transport protein relies on the chloride ion to increase the blood’s capacity of carbon dioxide, in the form of the bicarbonate ion.
- POTASSIUM: A crucial mineral that regulates body electrolyte balance. Deficiency can cause heart arrest, hypertension, adrenal exhaustion and muscular collapse.
- CALCIUM: The most abundant mineral in the body, it is especially important to bone and dental health, but is also involved in neural transmissions to the muscles. Spirulina in BAC supplies about as much calcium, gram for gram, as milk. Chlorophylls in BAC also contains rare calcium-spirulan, a well-known agent for its antibacterial, anti-fungal and anti-inflammatory benefits known to be effective against the AIDS virus.
- MAGNESIUM: Deficiency can lead to spasmodic muscle disorders, including cardiac irregularities. Helps assimilation of vitamin C, B vitamins and protein.
- PHOSPHORUS: The second most abundant mineral in the human body, it is found in practically every cell. Functions with calcium to maintain bone density. Helps to digest carbohydrates and the B vitamins niacin and riboflavin.
- SODIUM: Sodium ions play a diverse and important role in many physiological processes. Excitable animal cells, for example, rely on the entry of Na+ to cause a depolarization. An example of this is signal transduction in the human central nervous system, which depends on sodium ion motion across the nerve cell membrane, in all nerves.
- SULFUR: Sulphur is an essential component of all living cells. It is found in the hair, nails and skin, and as much sulphur as potassium is normally found in the body. Sulphur is used to detoxify the body, assist the immune system and fight the effects of ageing, as well as age related illnesses such as arthritis. Sulphur is an essential element of protein, biotin as well as vitamin B1. It is part of the chemical structure of the amino acids methionine, cysteine, taurine and glutathione. It is further needed in the synthesis of collagen, which is needed for good skin integrity.
Trace Elements
Bio-Algae Concentrates (BAC) contains some amount of all known trace elements occurring in a most human friendly form, that is naturally occurring from the plant kingdom.
In biochemistry, a trace element is a chemical element that is needed in minute quantities for the proper growth, development, and physiology of the organism. For this reason, in biochemistry they are also called micronutrients.
For example, iron found in BAC occurs in a non-toxic form that is more readily absorbed than that found in beef liver. Unlike iron from a bottle of iron supplement, its iron is like that of any plant such as celery or spinach and is vital for the body.
Here is a partial list and value discussion of a few trace elements found in BAC:
- BORON: Boron enhances the body’s ability to use calcium, magnesium, as well as vitamin D. It is also reported to assist in brain functioning and recognition. Boron seems to prevent calcium and magnesium from being lost in the urine and may help with decreasing menstrual pain by increasing the oestradiol level, which is a very active type of oestrogen. Boron may help with menopausal symptoms as well as maintaining healthy bones, because of its affinity to calcium and magnesium. It may also have to do with reduction of arthritis symptoms.
- CHRONIUM: Chromium is an essential nutrient required for normal sugar and fat metabolism and works primarily by potentiating the action of insulin. It is present in the entire body but with the highest concentrations in the liver, kidneys, spleen and bone. Although chromium is only required in very small amounts, our modern day diet has left many people short of chromium on a daily basis, with the average American being chromium deficient, and two out of three being hyperglycemic, pre-hyperglycemic or diabetic. Chromium is needed for energy, maintains stable blood sugar levels. In cooperation with other substances, it controls insulin as well as certain enzymes. It works with GTF (Glucose Tolerance Factor) when this hormone-affiliated agent enters the bloodstream because of an increase of insulin in the bloodstream.
- COBALT: Cobalt is part of the vitamin B 12 molecule. It is required in the manufacture of red blood cells and in preventing anaemia. In an average diet, deficiency is unlikely.
- COPPER: Copper and zinc absorption is closely related, and although copper is also needed in relatively small amounts, some discussions are under way on the optimum need of this mineral. If large amounts of copper are present, then zinc and vitamin C is reduced in the body, and vice versa. Copper is required in the formation of haemoglobin, red blood cells as well as bones, while it helps with the formation of elastin as well as collagen – making it necessary for wound healing. A lack of copper may also lead to increased blood fat levels. It is also necessary for the manufacture of the neurotransmitter noradrenaline as well as for the pigmentation of your hair.
- FLUORINE: Fluorine is a constituent of bones and teeth, but since it is very seldom added to supplements, we have not included a large volume of data on this element. It is beneficial in most cases in preventing dental caries, but the addition of fluoride to drinking water has become a controversial subject in some societies.
- IODINE: Iodine in our food is dependent on the iodine found in the ground where the food is grown, in the food the animals receive, as it influences the iodine content in the meat and eggs we consume. Iodine is used in the production of hormones (such as thyroxine, thyroxin) by the thyroid gland, which in turn regulates the conversion of fat to energy, stabilising our body weight as well as controlling our cholesterol levels. These hormones produced from the iodine are also needed to help form our bones, as well as keeping our skin, nails, hair and teeth in prime condition. Some indication also exists that iodine is helpful in preventing cancer of the breast and womb.
- IRON: Promotes formation of haemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying blood pigment found in healthy red blood cells. Iron deficiency is most common among women in their reproductive years.
- MANGANESE: Activates enzyme systems, along with zinc. Promotes activity of neurotransmitter acetylcholine, and helps stabilise blood sugar.
- MOLYBDENUM: Molybdenum is a component of three different enzymes, which is involved in the metabolism of nucleic acids – DNA and RNA – iron as well as food into energy. These three enzymes are sulfite oxidase, xanthine oxidase and aldehyde oxidase. Molybdenum assists in the breaking down of sulfite toxin build-ups in the body, and may prevent cavities. With these qualities, there might be evidence of antioxidant properties in this nutrient. It assists the body by fighting the nitrosamines, which are associated with cancer, and may help to prevent anaemia. It is needed for normal cell function and nitrogen metabolism. Molybdenum deficiencies in older males have also been linked to impotence and may be of value in fighting mouth and gum disorders. Molybdenum is part of sulfite oxidase, an enzyme that breaks down sulfites. Sulfites are found in protein food as well as chemical preservatives in certain foods and drugs. Should your body not be able to break down these sulfites, a toxic build-up results and your body may show an allergic reaction. These allergic reactions can be respiratory problems such as asthma and others. Molybdenum is also part of xanthine oxidase and aldehyde oxidase – both involved in the body’s production of genetic material and proteins. Xanthine oxidase also helps the body to oxidise purines and pyrimidines and produce uric acid, an important waste product.
- SELENIUM: Originally believed to be a toxic heavy metal, but now known to be necessary for health. It retards ageing, harmful oxidation and free radical formation, reduces the toxic effect of carcinogens, and improves cardiac efficiency.
- SILICON: Silicon is not present in the body in large amounts, yet is found in virtually every type of tissue in the body. Do not confuse it with silicone. Silicon is also called silica and is a natural substance while silicone is a man-made industrial polymer used in breast enlargement operations. Silicon is used to keep bones, cartilage, tendons and artery walls healthy and may be beneficial in the treatment of allergies, heartburn and gum disease, as well as assisting the immune system. It is also required by the nails, hair and skin to stay in good condition and is useful in counteracting the effects of aluminum. Silicon levels drop as we age, and it might therefore be beneficial as an anti-ageing component in our diets.
- ZINC: The pivot point of over thirty vital enzymatic reactions, with profound effects on mental health, skin tone, prostate function and healing capacity.
Fatty Acids
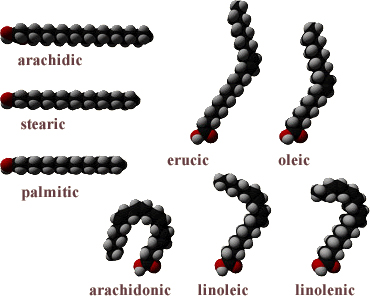
Bio-Algae Concentrates (BAC) contains Omega 3, 6, 9, GLA and several more including some yet undocumented or undiscovered.
Most of us think of fatty acids as oils coming from fish or seeds. You will be happy to learn that BAC is a rich source and is especially high in GLA, which is a critical nutrient that is universally lacking in our diets.
BAC contains Omega 3, 6, 9, GLA and many more fatty acids.
The human body uses fatty acids from food for building tissues and for specialised functions such as the production of prostaglandins, localized tissue hormones. One major group of fatty acids is called essential fatty acids, which are polyunsaturated, and include two major groups, omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. They are called “essential” because the body cannot make them but must get them from food.
The terms omega-3 and omega-6 actually designate two families of fatty acids; the former has the first double bond on the third carbon from the end of the fatty acid chain and the latter has the first double bond on the sixth carbon from the end of the fatty acid chain. The first fatty acid in the omega-6 family is called Linoleic Acid. It contains 18 carbons and has 2 double bonds.
Essential fatty acids (EFA) “the good fats that heal” are the fats you’ve been increasingly hearing about in recent years. Your body can’t live without them. They’re needed for a healthy heart, a healthy nervous system, a healthy immune system and especially a healthy brain (the human brain is around 80% fat).
The essential fatty acids sometimes called vitamin F, include linoleic, linolenic, arachidonic acid and many more. Some EFA’s are used by the body to manufacture Prostaglandins. These are the hormonal regulators of blood pressure and capillary resilience.
The essential fatty acids are involved in respiration in all the cells, and are especially important in oxygen transport. They affect the health of the hair, skin and nails, and help break up cholesterol in the blood stream. They are not dangerous fat but are absolutely vital to health.
If you’ve read anything about low-carb dieting or the “Mediterranean Diet,” you know that the consumption of healthy oils containing these fatty acids, produces astounding health benefits in the human body. Heart disease and various cardiovascular disorders respond quickly and positively. Brain function is improved, diabetes is brought under control, blood sugar is regulated, and cancer risk soon plummets.
Gamma linolenic acid (GLA) in BAC stimulates master hormones
Perhaps you’ve heard of GLA (gamma-linoleic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid). Human breast milk is high in GLA, probably due to the infant child’s need for brain-building fats. And since many infants never gained the important nutritional benefits of their mothers’ milk, they’ve been GLA-deficient for their entire lives. A diet of processed foods contains virtually no GLA. Low-carb dieters aren’t getting any either, unless they specifically supplement it.
GLA is not only known for regulating blood sugar and providing important nutrients to the brain; it also exhibits immune-boosting properties. In fact, according to Dr. Hass, author of Staying Health With Nutrition, GLA has been shown to be effective for the following health conditions:
- Cardiovascular disease – anti-inflammatory effect; reducing platelet aggregation, thereby reducing clotting; lowering blood pressure by decreasing vessel tone; cholesterol-lowering effect.
- Arthritis (rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory disorders) – anti-inflammatory effect; immune support; correcting possible EFA and GLA deficiency.
- Skin disorders (eczema, acne, dermatitis) – anti-inflammatory effect; EFA functions; immune support.
- Allergies, asthma – anti-inflammatory effect; EFA function; immune support.
- Multiple sclerosis – nerve conduction; correction of possible EFA and GLA deficiency; immune support; decreased platelet aggregation; balancing prostaglandins.
Essentially, GLA helps to support the immune system through a variety of mechanisms, but its benefits go far beyond immune system function. Many studies on the health effects of GLA have been conducted, and they show stunning results for this beneficial nutrient. In fact, in the 1980s, GLA was studied more intensively than any other nutrient: About 200 clinical trials took place in university hospitals and medical schools throughout the world. One of these researchers, Dr. Horrobin states “that his studies have led him to believe that a lack of essential fatty acids could turn out to be one of the most common defects in human biochemistry and a significant factor in many diseases”. Essential fatty acids are especially important in the function of nervous, muscular, and immune systems. When people lack the proper balance, the neurological, endocrine, and immune systems are shown to be adversely affected.
GLA has proven to be effective in the treatment of many serious diseases. Double-blind, placebo-controlled studies for atopic eczema demonstrate that GLA improves skin conditions, relieves itching, and reduces the amount of steroid medication required. In a large, placebo-controlled trial at Bristol University in England, both adults and children showed substantial improvements. In clinical trials for diabetes, GLA has reversed neurological damage and lowered plasma cholesterol and triglycerides. GLA has also been shown to be beneficial in the treatment of Sjogren’s Syndrome. –Innocent Casualties: The FDA’s War Against Humanity by Elaine Feuer-
Gamma Linolenic Acid (GLA) is a precursor for the body’s prostaglandins, master hormones that control many body functions. The prostaglandin PGE1 is involved in many tasks including regulation of blood pressure, cholesterol synthesis, cell proliferation and as an anti- inflammatory.
Foods high in saturated fats, typical of the contemporary diet, may block the beneficial work of essential fatty acids in the human body, leading to many disease conditions. Numerous studies have shown GLA deficiency may figure in degenerative diseases and other health problems. Clinical studies show that dietary intake of GLA can help arthritis, heart disease, obesity, and zinc deficiency. Alcoholism, manic-depression, ageing symptoms and schizophrenia also have been ascribed partially to GLA deficiency. A source of dietary GLA may help conditions of heart disease, premenstrual stress, obesity, arthritis and alcoholism. In Spain, the GLA in spirulina and evening primrose oil is prescribed for treatment of various chronic health problems.
The few known sources of GLA include the plant seed oils of evening primrose plant, blackcurrant and borage seeds, fungal oils, certain algae and human milk but you can also get it from BAC every day of your life!
Chlorophyll
Spirulina in BAC is one of the richest sources of chlorophyll with a perfect balance of magnesium. All plants, algae, and cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) that photosynthesize contain chlorophyll usually with the proper balance of levels of magnesium required for photosynthesis.
Chlorophyll, the Sheppard of Light
Energy are vital forces we associate with light having to do with liberating the sun’s forces from carbohydrates and lipids so we can use those forces to produce energy.
Certain microalgae like cyanobacteria in BAC are the only plants able to transfer sunlight energy into chemical energy with near 100% efficiency.
Energy from light is received somewhat directly as sunlight, but it is received in much greater amounts from our food. The chemical energy stored by photosynthesis in carbohydrates drives biochemical reactions in nearly all living organisms. Releasing the forces of light from food requires a balanced assembly of starches, sugars, and fats.
Chlorophyll is the shepherd of light energy – in the central atom of the chlorophyll molecule is magnesium where the sun’s light is gathered for releasing the sugars, starches, and fats from which we will eventually get our energy. Magnesium is omnipresent in the catabolic steps in which we disassemble sugars and fats in our metabolic fire: the Krebs (citric acid) cycle.
Thus, chlorophyll is at the centre of the photosynthetic oxidation-reduction reaction between carbon dioxide and water.
Chlorophyll and Blood Regeneration
Chlorophyll is sometimes called “green blood” because of its similarity to the haemoglobin molecule found in human blood cells. In fact, both are constructed of an almost identical molecular structure called pyrrole rings, and both substances are chemically known as “porphyrin pigments” by scientists. The difference is that chlorophyll contains a magnesium ion at its core, while haemoglobin contains an iron molecule. Magnesium imparts a green color to the chlorophyll molecule and is involved in synthesis of other materials, while iron gives haemoglobin a red colouration and changes the function of the porphyrin molecule to respiration and breakdown of materials. But perhaps the most interesting connection between green foods and blood is the similarity in the structures of the two coloured pigments, heme and chlorophyll.
What’s so good about the chlorophylls in BAC?
BAC’s most visible pigments are chlorophylls. There’s nothing more supportive to cleansing than chlorophyll. People who follow Western diets (high in processed foods and animal foods) are in desperate need of cleansing.Beside energy and cleansing, there are many associated benefits to chlorophylls:
- Chlorophylls release ions when struck by the energy of sunlight. These free ions proceed to stimulate the biochemical reactions that form proteins, vitamins and sugars.
- It increases peristaltic action and thus relieves constipation, and also normalises the secretion of digestive acids.
- It soothes the inflammation and reduces the excess pepsin secretion associated with gastric ulcers.
- It supports liver function so that your body can do a better job of eliminating toxins from your system.
- It is believed that if chlorophyll is ingested with sufficient iron, the magnesium can be displaced to yield a haemoglobin molecule.
- Experiments in Japan and Russia have demonstrated that algae have a marked positive effect on leukemia and anaemia, possibly due to the conversion of chlorophyll into haemoglobin.
Polysaccharides
The algae found in Bio-Algae Concentrates (BAC) have an unique cell wall made of complex polysaccharides, which have been shown to stimulate interferon production and exhibit strong anti-tumour activity in a series of studies conducted over the last several decades.
Polysaccharides are relatively complex carbohydrates. They are polymers made up of many monosaccharides joined together by glycosidic bonds. Cell-surface polysaccharides as in microalgae like spirulina in BAC play diverse roles in the bacterial “lifestyle”. They serve as a barrier between the cell wall and the environment, mediate host-pathogen interactions.
Studies on the consumption of food-grade microalgae have reported enhanced immune function in animals and humans.
- Dietary spirulina has been shown to exhibit chemopreventive and antiviral effects in humans. The active component for these effects has been investigated; it appears that several types of polysaccharides exhibit biological activity.
- Calcium spirulan inhibits replication of several enveloped viruses. These include herpes simplex, cytomegalovirus, mumps and measles viruses, influenza A virus, and HIV-1.
- Another polysaccharide found in spirulina, immunlina, has been shown to activate monocytes and macrophages
- Spirulina polysaccharides are clinically observed to provide immune system modulation and reduction of blood sugar level to normal.
- Scientists also found that spirulina’s polysaccharide acts similarly to Phycocayanin, a highly potent agent that activates the immune system. It improves the immune system’s ability to detect and destroy foreign microbes or eliminate toxins. It also enhances T-cells and improves Thymus gland function. Also observed were increased antibody levels and normalisation of other cellular functions.
- Calcium spirulina, from a blue-green algae spirulina enveloped virus replication, – Hayashi et al. 1996. Pub. In Journal of Natural Products, Vol. 59, p. 83-87. Japan.
Phytonutrients
The Bio-Algae Concentrates (BAC) formulations with their mix of blue-green, brown and red microalgae contain thousands of phytochemical and colourful pigments making up the entire colour spectrum found in nature from blue to green and red.
We know today that the principal nutrients for prevention of cancers are found in colourful fruits and vegetables (American Cancer Society). Those nutrients are a mix of phytonutrients such as antioxidants, carotenoids, chlorophils and other compounds found in those fruits and vegetables.
There is abundant evidence from epidemiological studies that the phytochemicals in fruits and vegetables can significantly reduce the risk of cancer, probably due to polyphenol antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
Phytochemicals have been used as drugs for millennia. For example, Hippocrates in 400 BC used to prescribe willow tree leaves to abate fever. Salicin as in Aspirin, with potent anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving properties, was originally extracted from the White Willow Tree.
In summary, BAC contains a large array of pigments and carotenes like beta carotene, alpha-carotene, astaxanthin, lutein, lycopene, quercitin, phycocyanine, phycobilins, b cryptoxanthin and several others that offer powerful immunity and toxin shield against continuous pollution, toxins and stress.
Antioxidants
Bio-Algae Concentrates (BAC) contains extraordinary antioxidant compounds and especially some like alpha-carotene and beta-carotene known as “pro-pro vitamin A” for their capacity to not only traverse cell membrane but to span across the cell membrane.
An Antioxidant is a molecule capable of slowing or preventing the oxidation of other molecules. Oxidation is a chemical reaction that transfers electrons from a substance to an oxidising agent. Oxidation reactions can produce free radicals, which start chain reactions that damage cells. Antioxidants terminate these chain reactions by removing free radical intermediates, and inhibit other oxidation reactions by being oxidised themselves.
It is also known today that orange and red pigments have the most antioxidative and protection powers due to their molecular shape and properties. For example, beta carotene, the orange pigments of carrots or the red licopene of tomatoes have molecular shapes allowing them to easily travel across the blood brain barrier, even across the blood iris barrier, hence the popular saying “you’ve never seen a rabbit wearing glasses”.
BAC contains high level of astaxanthin, the star of antioxidants Astaxanthin is a pigment of the carotenoid complex found in the microalgae Haematococcus pluvialis present in BAC. It is an oxygenated pigment called a xanthophyll. Its unique molecular structure gives it a superior antioxidant capacity.
Benefits of Astaxanthin:
- 10 to 40 times more effective as an antioxidant than beta-carotene
- 500 to 1000 times more effective in inhibiting lipid peroxidation as an antioxidant than Vitamin E
- Has greater anti-inflammatory capability than Vitamin E
- Has almost 4 times the antioxidant capacity of lutein
- Offers superior protection against UVA and UVB light-induced oxidative stress more stable in scavenging and quenching than b-carotene canthaxanthin and zeaxanthin
- Highly potent in enhancing T1 and T2 cancer killing helper cells production
- More effective than lycopene and lutein in enhancing liver microsome detoxification activity
- Enhances the actions of Vitamins C and E in the body
- Enhances the release of retinol (Vitamin A) from the liver
Carotenoids
Bio-Algae Concentrates (BAC) contains an extraordinary number of yellow/orange pigments called carotenoids.
Carotenoids are organic pigments that are naturally occurring in plants and some other photosynthetic organisms like algae, some types of fungus and some bacteria. There are over 600 known carotenoids; they are split into two classes, xanthophylls and carotenes. They absorb blue light.
Until late in the 20th Century, the functions of these carotenoids were discussed only in terms of their potential vitamin A activity. However, it has since been discovered that certain members of the carotenoid family, approximately 50 carotenoids of the known 600, are called “pro vitamin A” compounds because the body can convert them into retinol, an active form of vitamin A.
BAC contains many of these yellow/orange pigments from which pro and pro-pro-vitamin A can be made. Here is a partial list:
- Alpha-carotene
- Beta-carotene
- Phycocyanin
- Xanthophylis
- Cryptoxanthin
- Echinenone
- Zeaxanthin
- Lutein
- Licopene
- Astaxanthin
- Etc
The extraordinary amounts of carotenoids and several lesser pigments such as phycoerythrin, tetrapyrrole, and phytonadione found in BAC are not just the “colour” of living organisms, but are used to carry on metabolic processes throughout the body. Without them, enzymatic reactions would be reduced until cellular disintegration occurred.